Measuring the Ambient temperature of Aluminum electrolytic capacitor
Accurately measuring the ambient temperature is critical to product lifetime estimation. Here, we use a video to explain the actual procedure.
Ambient temperature measurement position
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors are often mounted adjacent to other parts (semiconductors, resistors, etc.), which means that failing to choose the appropriate measurement position can result in significant measurement errors.For layouts where multiple capacitors are connected in parallel or in a series, it is ideal to measure the ambient temperature for all capacitors but there are cases when this will prove difficult. In such cases, one possible method is to select capacitors in positions most likely to be affected by heat during operation, and measure the ambient temperature of those capacitors.
In this example, we ran the device for a specified time and then used thermography to observe the device and identify positions most likely to be subjected to heat. We then measured the ambient temperature at those positions.
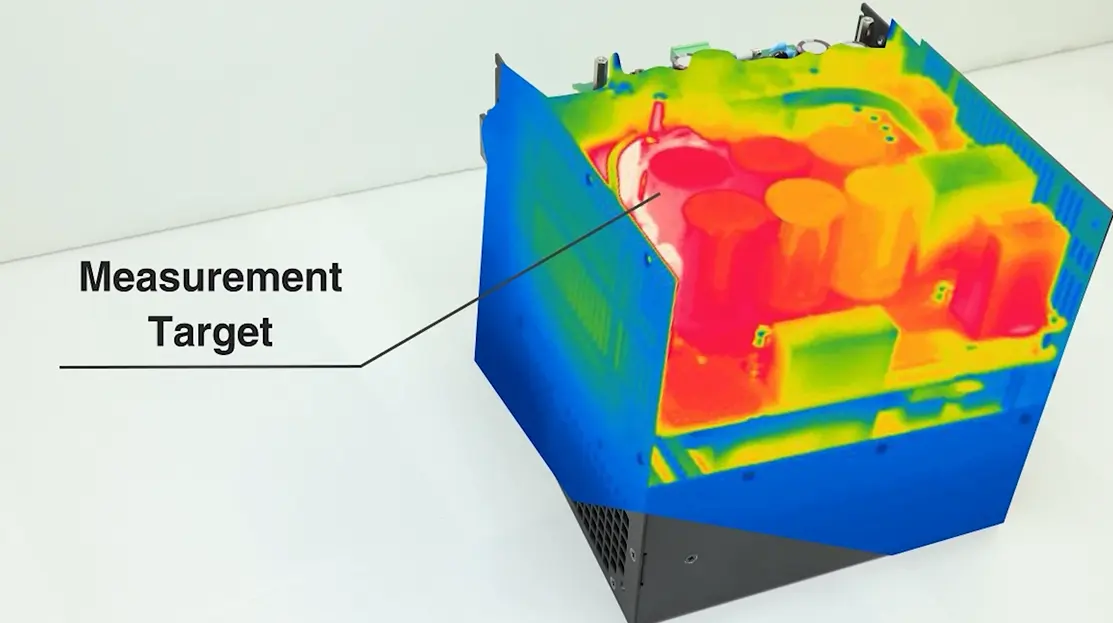
Fig.1 Thermography image(example)
The term “ambient temperature” is often thought to refer to the temperature of the air around the capacitor. However, we define ambient temperature as the temperature of a capacitor impacted only by radiant heat (heat convection, heat radiation, heat conduction) at the specific position.
A capacitor in a state of being impacted only by radiant heat is called a dummy capacitor. These capacitors are mounted in an electrically insulated state so measuring the surface temperature of these capacitors enables the precise measurement of the impact of radiant heat only (capacitor ambient heat).
Fig.2 Concept diagram of radiant heat
Method of measurements using dummy capacitors
- Remove the aluminum electrolytic capacitor from the measurement position.
- Connect the removed capacitor to the circuit electrically using a lead line.
We recommend using a large-diameter cable for the lead line to ensure the lowest possible impedance. - Preparing the dummy capacitor
The dummy capacitor should not be self-heating. In other words, it should be electrically insulated.
In this example, we severed the terminal on one side and covered it with insulating tape.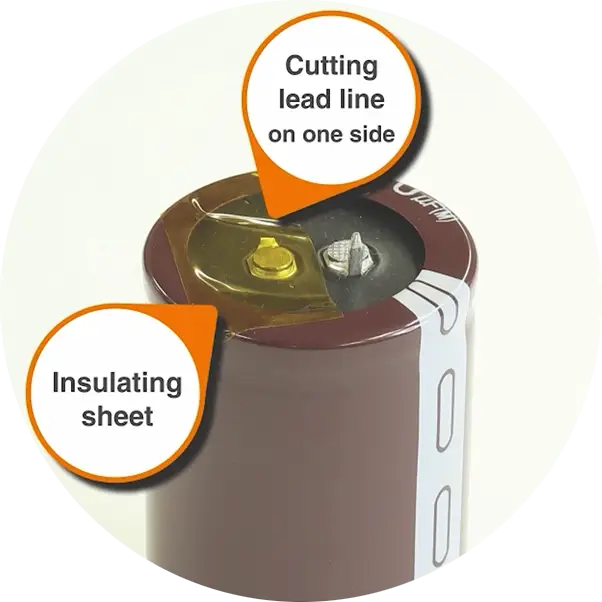
Fig.3 Dummy capacitor insulation example
- Mounting the dummy capacitor
Mount the dummy capacitor to the same position as the capacitor you removed.
To increase the reproducibility of thermal conduction, solder the terminal on the un-severed side. - Attaching a thermocouple to the dummy capacitor
The surface temperature of the dummy capacitor will be considered the ambient temperature.
As heat convection occurs from all directions, attach a thermocouple to four points, with the average value to be used as the ambient temperature. - Reproduce same conditions as operating conditions
If there is a chassis cover or a forced air-cooling system, then reproduce the same conditions as those used for actual operation. - Measuring ambient temperature
Once you achieve the same conditions as actual operating conditions, then operate the device at the assumed load and record the temperature change.
For a device used in continuous operation, use the measurement value read when temperature saturation is reached as the ambient temperature.
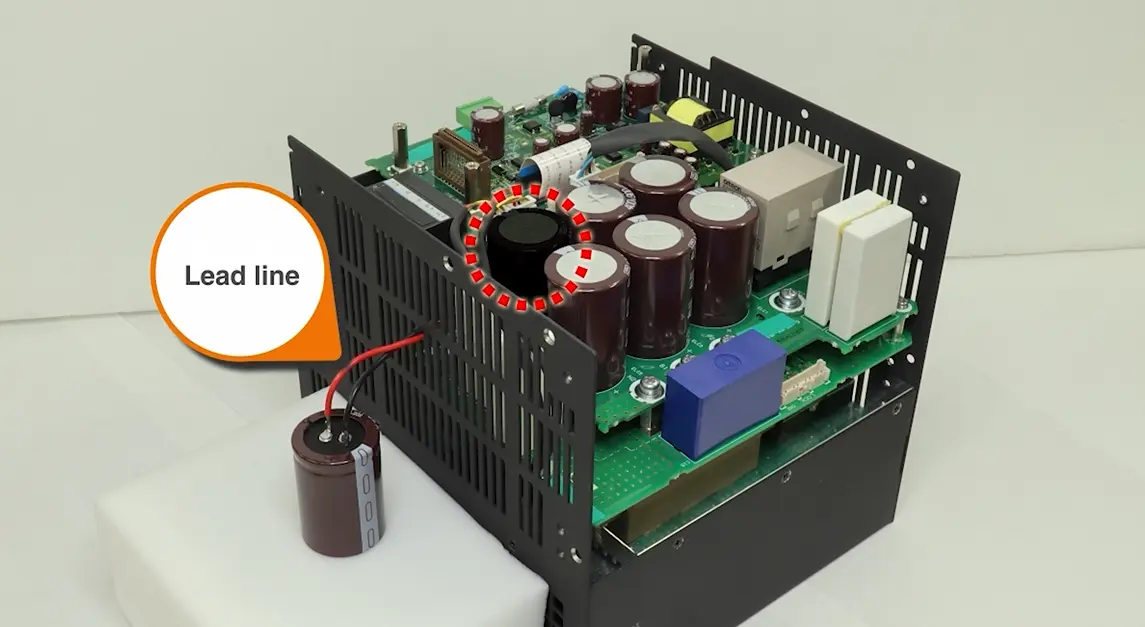
Fig.4 Dummy capacitor with lead capacitor connected
Use for lifetime estimation
You can use the measured ambient temperature to estimate lifetime.We offer an online service for estimating lifetime that is available for use.
Useful information
If you have any questions or inquiries that do not apply to the above, please contact us at the following address.